Knee osteoarthritis and hyaluronic injection

The knee is the largest and strongest joint in our body. It is made up of the lower end of the femur -thighbone, the upper end of the tibia - shinbone, and the patella better known as a kneecap. The ends of the three bones that form the knee joint are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth, slippery substance that protects and cushions the bones as you bend and straighten your knee.
Very important components of the knee joint are meniscus. Two wedge-shaped pieces of cartilage acts as shock absorbers between your thighbone and shinbone. They are tough and rubbery to help cushion the joint and keep it stable.
The knee joint is surrounded by a thin lining called the synovial membrane. This membrane releases a fluid that lubricates the cartilage and reduces the friction.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a chronic and progressive process of destruction the normal structure of the joint, which consists of degeneration of articular cartilage, ligaments, joint capsule and other elements forming the knee joint.
There are two basic forms of knee osteoarthritis, primary and secondary. The most common is the primary form, which results from degenerative changes occurring with age, which may be intensified by risk factors such as obesity, repetitive joints use, gender, improperly selected physical activity. The secondary form is caused by a specific causative factors such as congenital joint defects, systemic diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, gout, etc., inflammatory process, genetic diseases, trauma.
In osteoarthritis, the cartilage in the knee joint gradually wears away. As the cartilage wears away, it becomes frayed and rough, and the protective space between the bones decreases. This can result in bone rubbing on bone and produce painful bone spurs. Osteoarthritis usually develops slowly and the pain it causes worsens over time.
Symptoms
A knee joint affected by osteoarthritis may be painful and inflamed. Generally, the pain develops gradually over time, although sudden onset is also possible. There are other symptoms, as well:
- The joint may become stiff and swollen, making it difficult to bend and straighten the knee.
- Pain located in the knee in the morning or after some period of sitting or resting
- Dynamic physical activity may cause pain worse
- Loose fragments of the cartilage and other tissues can interfere with the smooth motion of the joint. The knee may lock or stick during movement. It may creak, click, snap, or make a grinding noise. We called it the noisy joints
- Pain may cause a feeling of weakness or buckling in the knee.
- Many people with arthritis note increased joint pain with changes in the weather.
Treatment
According to the latest data, the focus should be primarily on preventing the occurrence of degenerative changes. Early diagnose and treatment of pathologies within the knee joint is of key importance here.
When the first symptoms of osteoarthritis are visible the best option is to see the Physiotherapist and create the initial treatment plan. The changes around the knee joint are not reversible, however there are methods which can delay the process and do not worse the symptoms.
There is many possibilities to deal with the pain knee syndrome, such as general physio, moderate physical activity. But the best option on the beginning is hyaluronic acid joint injection.
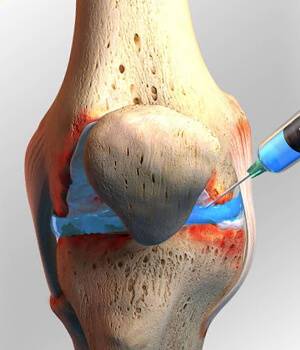
Hyaluronic Injection with the Knee osteoarthritis
Hyaluronic acid injections are used to treat knee osteoarthritis and improve the functions of the knee joint. This treatment method is called viscosupplementation. During a hyaluronic acid injection a small amount of hyaluronic acid, often just 2 mL, is injected directly into the knee joint capsule. The effects of the injection are:
- Reduce the pain and stiffness
- Improve joint movement by increasing joint lubrication and reducing joint friction and inflammation
- Slow down the osteoarthritis progress
- Protects the joint from wear and tear
- Works as a shock absorber, protecting the cartilage
The most of our patients who had the hyaluronic injections confirms the above effects around 3-6 weeks after first injection. The duration of pain relief following a Hyaluronic Acid Injection is generally longer than a Cortisone Injection in patients with Mild-moderate knee arthritis. Cortisone works very quickly, but on average only lasts around 4 months, whereas Hyaluronic Acid Injections are slower to work, but often provide relief for 6-9 months. Very valuable fact is that cortisone injections work as a pain blocker, with no joint protection, where hyaluronan brings pain relief effects, protects the joint at the same time.